Formats and Purposes
Email remains one of the most powerful tools in digital communication—whether you’re connecting with family, closing a business deal, or nurturing your audience through marketing automation. But not all emails are created equal. They differ in format and purpose, and understanding these distinctions helps you write clearer messages, improve engagement, and choose the right style for every situation.
Below is a breakdown of the primary email formats and the various types of emails used in personal, professional, and marketing communication.
Email Formats: How Emails Are Built
Email “format” refers to the way the message is structured and displayed. Some formats are simple and distraction-free, while others offer advanced design capabilities that make them visually appealing.
1. Plain Text
Plain text emails contain only text—no bolding, no images, no colors, and no special layout.
Best for:
-
Personal emails
-
Minimalist communication
-
Delivering messages that must be readable on any device or system
Plain text is valued for its simplicity and reliability. It loads quickly, works everywhere, and feels personal.
2. Rich Text
Rich text allows for basic formatting, such as:
-
Bold and italic text
-
Different font styles
-
Bulleted or numbered lists
Best for:
-
Professional communication
-
Emails requiring emphasis without full graphic design
-
Internal company correspondence
Rich text is a step up from plain text, offering clarity and visual structure without the complexity of coding or design.
3. HTML Email
HTML emails are the most visually robust format, supporting:
-
Images
-
Buttons
-
Links
-
Custom layouts
-
Branding and color schemes
Best for:
-
Marketing emails
-
Newsletters
-
Product announcements
-
Automated campaigns
Because HTML emails can mirror the look of a web page, they are ideal for storytelling, promotions, and brand presentation. However, they require more design and testing to ensure compatibility across devices and email clients.
Email Retrieval Protocols
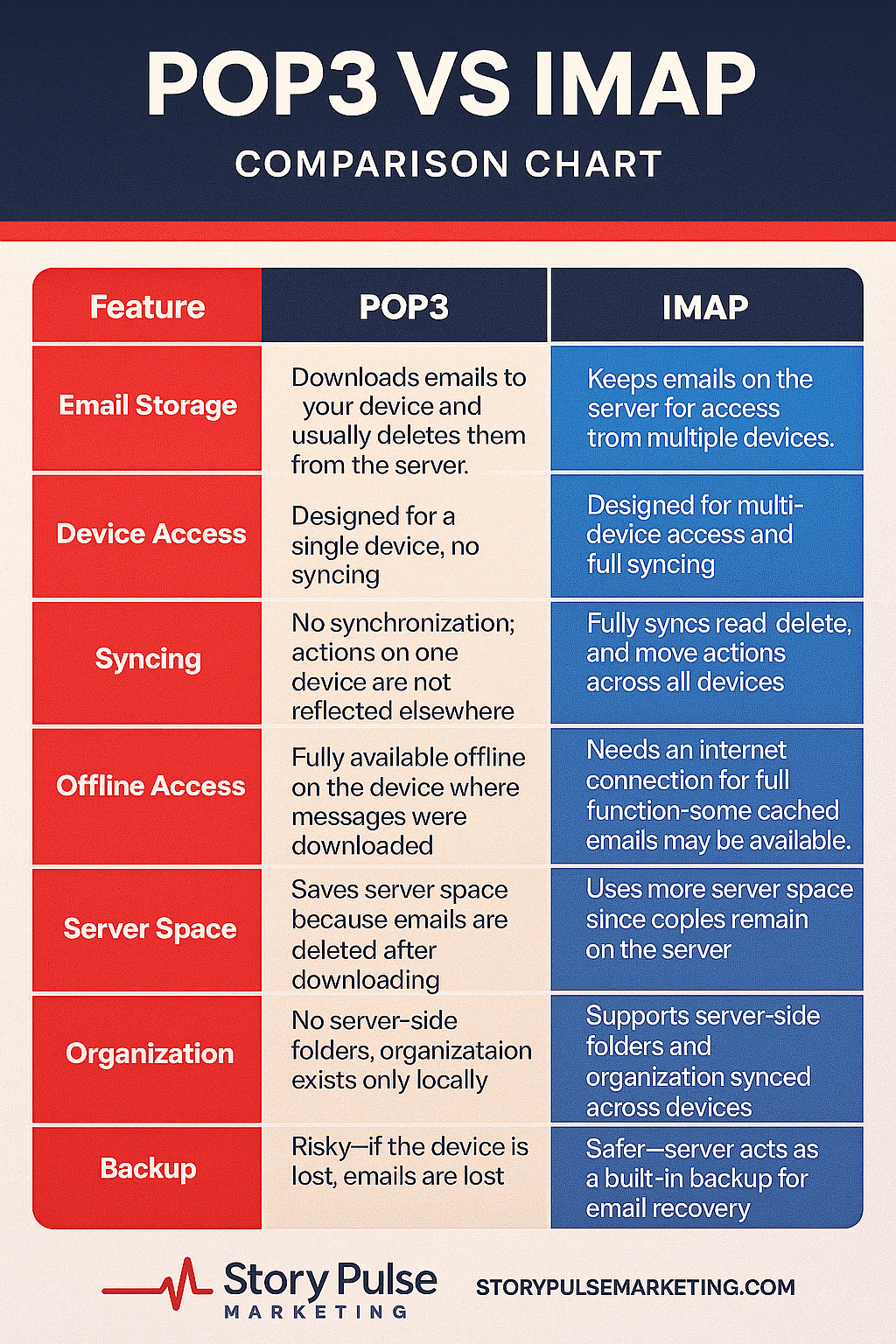
POP3 and IMAP Are NOT Types of Emails — They Are Email Protocols
POP3 and IMAP are email retrieval protocols.
They control how your email program (like Outlook, Apple Mail, Gmail app) gets messages from the mail server.
They are not types of emails (like newsletters, transactional emails, or personal emails).
They are not email formats (like plain text, rich text, or HTML).
They are simply methods for accessing your inbox.
Email Purposes: Why Emails Are Sent
Beyond formatting, emails also can be categorized by purpose—what the message is meant to accomplish. Understanding these groups helps create emails that meet audience expectations and achieve specific goals.
1. Personal Emails
Personal emails are informal and conversational. They are typically used for communicating with:
-
Friends
-
Family
-
Acquaintances
These messages focus on personal matters without the structure or tone required in professional settings.
2. Professional Emails
Professional emails follow a more formal tone and structure. They are used for:
-
Workplace communication
-
Business proposals
-
Client interactions
-
HR and administrative coordination
Professional emails are expected to be concise, clear, and courteous.
3. Marketing Emails
Marketing emails are sent by businesses and organizations to engage audiences, build relationships, and drive action. Common types include:
• Newsletters
Sent on a predictable schedule, newsletters share updates, articles, announcements, and curated content to keep readers connected to your brand.
• Promotional Emails
Highlight special offers, discounts, product launches, or limited-time deals designed to encourage purchases.
• Welcome Emails
Sent to new subscribers or customers to introduce your brand, set expectations, and build trust.
• Abandoned Cart Emails
Triggered when a shopper leaves items in an online cart. These emails remind them to complete the purchase—often including an extra incentive like free shipping or a small discount.
Marketing emails are often automated and heavily benefit from HTML formatting for visual appeal and analytics tracking.
4. Transactional Emails
Transactional emails are automatically triggered by a user action. Examples include:
-
Order confirmations
-
Shipping notifications
-
Password resets
-
Appointment reminders
These emails contain essential information and typically use straightforward layouts to ensure clarity and reliability.
5. Educational Emails
Educational emails aim to teach or inform the reader. They might include:
-
Tutorials
-
Product tips
-
How-to guides
-
Industry insights
These emails add value by helping the reader learn something new while building credibility for your brand.
6. Re-Engagement Emails
Re-engagement emails target subscribers who have stopped opening or interacting. Their goal is to restore interest through:
-
Special offers
-
“We miss you” messages
-
Updated content preferences
-
Exclusive content invitations
These campaigns help clean your list and restore lost connections.
Conclusion
Email is far more versatile than it may seem. Whether you’re crafting a simple personal message or a branded HTML campaign, understanding the format and purpose ensures your communication is effective, engaging, and appropriate for your audience.

